Episode #4 - From Code to Cure: How DNA Writes the Protein Blueprint
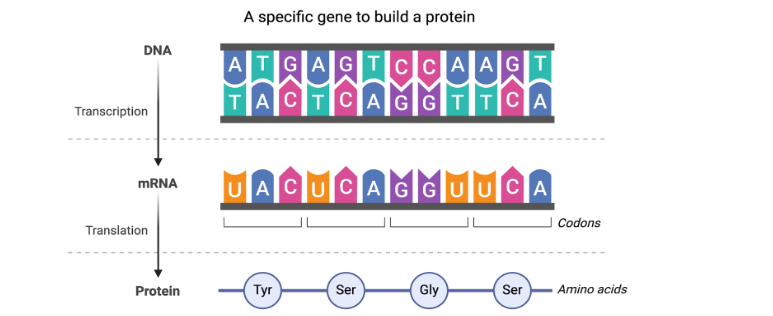
This schematic illustrates the process of using DNA to create proteins. First, the information in DNA is copied into mRNA during a process called transcription. The next step is translation, whereby the mRNA is read in groups of three nucleotides known as codons to form a protein. Each codon represents an amino acid.
Types of Mutations to DNA
This figure illustrates how different DNA mutations can affect the mRNA sequence and the resulting protein. The “Normal sequence” in the top-left panel shows an mRNA sequence with no mutations, producing a functional protein. In the top-right panel, a “Base-pair deletion” removes a single nucleotide, causing a frameshift mutation that alters the reading frame and changes the resulting amino acids. The bottom-left panel shows a “Base-pair insertion,” where an extra nucleotide causes an immediate stop codon, leading to a shortened, nonfunctional protein. The bottom-right panel shows a “Three-nucleotide insertion/deletion,” which removes or adds a whole codon, leading to the loss or addition of an amino acid without shifting the reading frame. However, it still affects the protein structure.